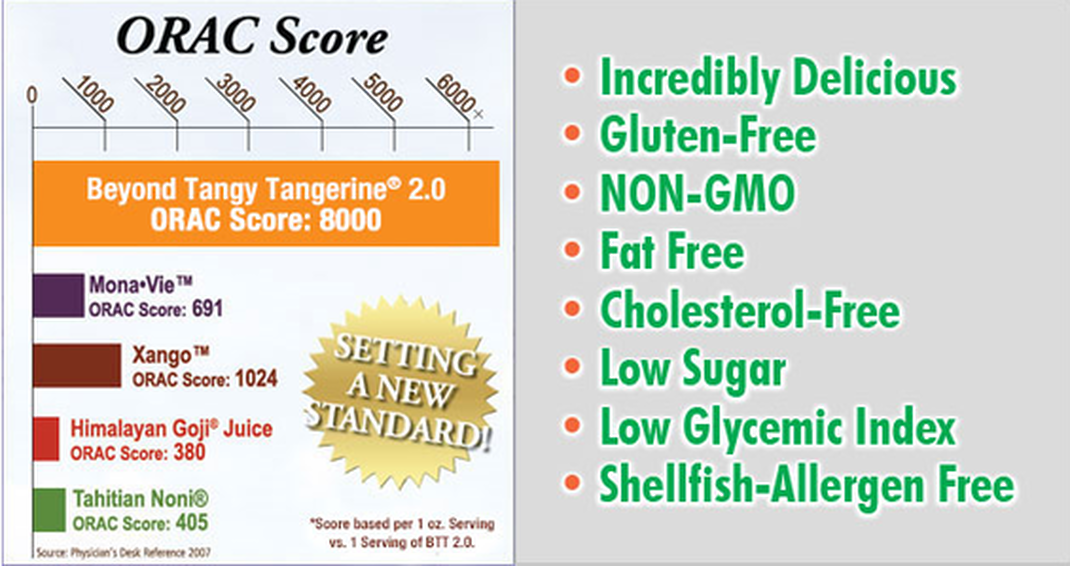
There’s no easier way to provide your body with essential nutrients. This multi-vitamin mineral complex contains whole foods, trace minerals, antioxidants, prebiotics and probiotics, amino acids and methylfolate. Plus, you get synergizing nutrients that help ensure maximum absorption in your body. And with an ORAC Score (antioxidant capacity) of 8,000, you get even more antioxidants to combat free radicals and support your overall health. Now improved, with more Beet Root powder, methylfolate added, and an improved taste of tropical tangerine!
BENEFITS Methylfolate
|
MTHFR specifically is a gene that holds the recipe for methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase - an enzyme that helps our bodies convert vitamin B9 (also known as folate) into a usable form called methyl-folate. This process is called methylation. The process of methylation is very important to overall health and occurs in every cell of the body. It is necessary for the detoxification of environmental toxins that have made it into the body. It helps enzymes in the body to work properly, and it effects the function of genes themselves.
|
The problem with the MTHFR gene is when it becomes mutated. When this happens, the process of methylation is hindered. This leads to all kinds of trouble. If your MTHFR gene has become mutated then you will not experience optimal health until you give your body Methyl-Folate (and sometimes Niacin - Vitamin B-l), because it cannot make it on its own - and it cannot convert Folate into Methyl-Folate.
It is important to note that the "folate" in most foods and vitamins is folic acid. When the MTHFR gene is functioning properly, it's highly efficient at helping our bodies convert vitamin B9 (folate) into a usable form called methyl-folate. When the gene is mutated, this capacity to convert vitamin B9 into methyl-folate is reduced by 40-70%.
It is important to note that the "folate" in most foods and vitamins is folic acid. When the MTHFR gene is functioning properly, it's highly efficient at helping our bodies convert vitamin B9 (folate) into a usable form called methyl-folate. When the gene is mutated, this capacity to convert vitamin B9 into methyl-folate is reduced by 40-70%.